Wavefront algorithm
Wavefront 演算法是BFS(廣度優先搜索)演算法的其中一種,常見於2D網格地圖中用以找尋路徑。在wavefront算法中,隊列以源節點初始化,算法通過按照節點距離源節點的特定順序將相鄰節點添加到隊列中來進行進展。這創建了一個從源節點向外擴展的“wavefront”。
1. 準備網格2D地圖
x1# A demo about wavefront algorithm2cols = rows = 203
4def setup():5 global spots6 size(800, 800)7 textAlign(CENTER, CENTER)8 rectMode(CENTER)9 spots = [[Spot(i, j) for i in range(cols)] for j in range(rows)]10
11def draw():12 background(51)13 for i in range(cols):14 for j in range(rows):15 spots[i][j].show()16
17class Spot:18
19 def __init__(self, _i, _j):20 self.w = width/cols21 self.h = height/rows22 self.i = _i23 self.j = _j24 self.x = _i * self.w + self.w/225 self.y = _j * self.h + self.h/226
27 def show(self):28 fill(255)29 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)
這裡介紹多一個可以快速開始2D list的方法。在以前的做法中,我們會用到兩個for loop,而在第一個for loop中會加入一個暫存的list,例子如下:
xxxxxxxxxx51for i in range(cols):2 temp = []3 for j in range(rows):4 temp.append(Spot(i,j))5 spots.append(temp)但其實可以用一個較簡單的方法。Python提供一個先寫結果,再寫condition的寫法,for loop和if都有這選項,不用每次為寫一個簡單的for和if都要分兩行來寫,另一個好處是可以很容易地做到巢狀的for和if。
xxxxxxxxxx11spots = [[Spot(i, j) for i in range(cols)] for j in range(rows)]2. 為每個格加入鄰居和加入牆
xxxxxxxxxx671# A demo about wavefront algorithm2
3cols = rows = 204spots = []5start = end = None6
7
8def setup():9 global spots, start, end10 size(800, 800)11 textAlign(CENTER, CENTER)12 rectMode(CENTER)13 spots = [[Spot(i, j) for j in range(rows)] for i in range(cols)]14 15 start = spots[0][0]16 end = spots[cols-1][rows-1]17 18 for i in range(cols):19 for j in range(rows):20 if spots[i][j] != start and spots[i][j] != end:21 spots[i][j].addWall()22 spots[i][j].addNeighbors(spots)23 24def draw():25 background(51)26 27 for i in range(cols):28 for j in range(rows):29 spots[i][j].show('#FFFFFF')30 start.show('#00FFFF')31 end.show('#FFFF00')32
33
34class Spot:35
36 def __init__(self, _i, _j):37 self.w = width/cols38 self.h = height/rows39 self.i = _i40 self.j = _j41 self.x = _i * self.w + self.w/242 self.y = _j * self.h + self.h/243 self.wall = False44 self.neighbors = []45
46 def show(self, _color):47 strokeWeight(0.5)48 stroke(127)49 if self.wall:50 fill(0)51 else:52 fill(_color)53 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)54
55 def addWall(self):56 self.wall = True if random(1) < 0.25 else False57
58 def addNeighbors(self, _spots):59 if self.wall == False:60 if self.j > 0 and _spots[self.i][self.j-1].wall == False:61 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i][self.j-1])62 if self.i < cols-1 and _spots[self.i+1][self.j].wall == False:63 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i+1][self.j])64 if self.j < rows-1 and _spots[self.i][self.j+1].wall == False:65 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i][self.j+1])66 if self.i > 0 and _spots[self.i-1][self.j].wall == False:67 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i-1][self.j])
xxxxxxxxxx111class Spot:2
3 def __init__(self, _i, _j):4 self.w = width/cols5 self.h = height/rows6 self.i = _i7 self.j = _j8 self.x = _i * self.w + self.w/29 self.y = _j * self.h + self.h/210 self.wall = False11 self.neighbors = []首先為Spot class加入self.wall變數,用來設定當前的格是否牆。另外再加入self.neighbors = []的空list,用來裝起每個格的鄰居。
xxxxxxxxxx131 def addWall(self):2 self.wall = True if random(1) < 0.25 else False3
4 def addNeighbors(self, _spots):5 if self.wall == False:6 if self.j > 0 and _spots[self.i][self.j-1].wall == False:7 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i][self.j-1])8 if self.i < cols-1 and _spots[self.i+1][self.j].wall == False:9 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i+1][self.j])10 if self.j < rows-1 and _spots[self.i][self.j+1].wall == False:11 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i][self.j+1])12 if self.i > 0 and _spots[self.i-1][self.j].wall == False:13 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i-1][self.j])加入兩個函數,隨機抽出0至1之間的任意值,如果是少於0.25的話,就將self.wall設定成True,否則就是False。
之後就將為每一個spot加入鄰居,如果鄰居不是牆,而且又不是邊緣的話,就將旁邊的spot加入做鄰居。這裡的做法跟第7章十分相似,如果忘記的同學可以參考第7章的7. Snake。
xxxxxxxxxx81def show(self, _color):2 strokeWeight(0.5)3 stroke(127)4 if self.wall:5 fill(0)6 else:7 fill(_color)8 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)最後將顯示顏色變成一個輸入的變數。
xxxxxxxxxx121def setup():2 global spots, start, end3 #(same as before)4 5 start = spots[0][0]6 end = spots[cols-1][rows-1]7 8 for i in range(cols):9 for j in range(rows):10 if spots[i][j] != start and spots[i][j] != end:11 spots[i][j].addWall()12 spots[i][j].addNeighbors(spots)在setup()中,加入start和end的位置,分別為於左上角和右下角。如果這個spot不是起點和終點的話,就隨機加入牆,之後就加入鄰居。
xxxxxxxxxx81def draw():2 background(51)3 4 for i in range(cols):5 for j in range(rows):6 spots[i][j].show('#FFFFFF')7 start.show('#00FFFF')8 end.show('#FFFF00')最後獨立將start和end顯示成不同顏色。
3. 為每個格打上分數
xxxxxxxxxx991# A demo about wavefront algorithm2
3cols = rows = 204spots = []5start = end = None6pathIsFound = False7path = []8queue = []9
10def setup():11 global spots, start, end12 size(800, 800)13 textAlign(CENTER, CENTER)14 rectMode(CENTER)15 spots = [[Spot(i, j) for j in range(rows)] for i in range(cols)]16 17 start = spots[0][0]18 end = spots[cols-1][rows-1]19 20 for i in range(cols):21 for j in range(rows):22 if spots[i][j] != start and spots[i][j] != end:23 spots[i][j].addWall()24 spots[i][j].addNeighbors(spots)25
26 start.visit()27 queue.append(start)28
29
30def draw():31 global pathIsFound, path, queue32 33 if len(queue) == 0:34 noLoop()35 return36
37 background(51)38
39 current = queue.pop(0)40 41 for neighbor in current.neighbors:42 if not neighbor.isVisited() and not neighbor.wall:43 neighbor.visit()44 neighbor.score = current.score + 145 queue.append(neighbor)46
47 for i in range(cols):48 for j in range(rows):49 spots[i][j].show('#FFFFFF')50 start.show('#00FFFF')51 end.show('#FFFF00')52 for spot in path:53 spot.show('#FF00FF')54
55
56class Spot:57
58 def __init__(self, _i, _j):59 self.w = width/cols60 self.h = height/rows61 self.i = _i62 self.j = _j63 self.x = _i * self.w + self.w/264 self.y = _j * self.h + self.h/265 self.wall = False66 self.neighbors = []67 self.visited = False68 self.score = 069
70 def show(self, _color):71 strokeWeight(0.5)72 stroke(127)73 if self.wall:74 fill(0)75 else:76 fill(_color)77 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)78 fill(0)79 text(self.score, self.x, self.y)80
81 def addWall(self):82 self.wall = True if random(1) < 0.25 else False83
84 def addNeighbors(self, _spots):85 if self.wall == False:86 if self.j > 0 and _spots[self.i][self.j-1].wall == False:87 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i][self.j-1])88 if self.i < cols-1 and _spots[self.i+1][self.j].wall == False:89 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i+1][self.j])90 if self.j < rows-1 and _spots[self.i][self.j+1].wall == False:91 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i][self.j+1])92 if self.i > 0 and _spots[self.i-1][self.j].wall == False:93 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i-1][self.j])94 95 def visit(self):96 self.visited = True97 98 def isVisited(self):99 return self.visited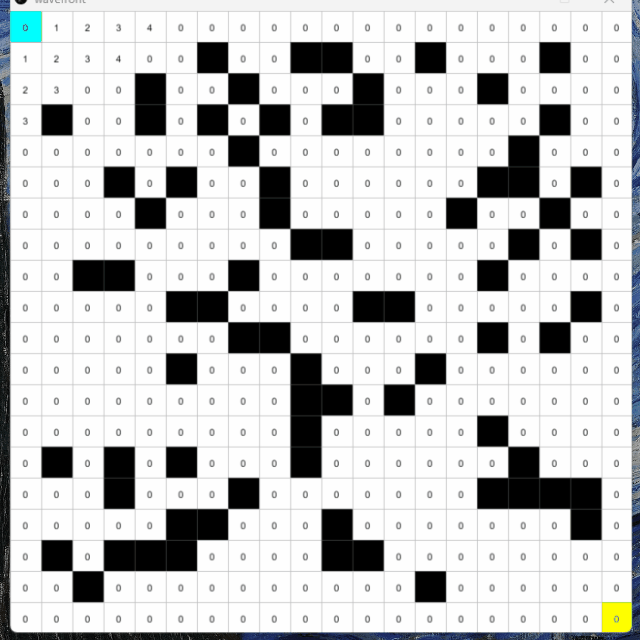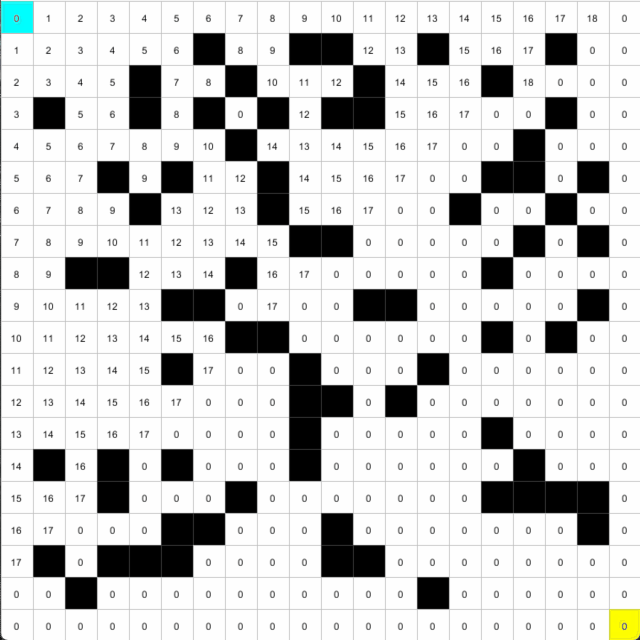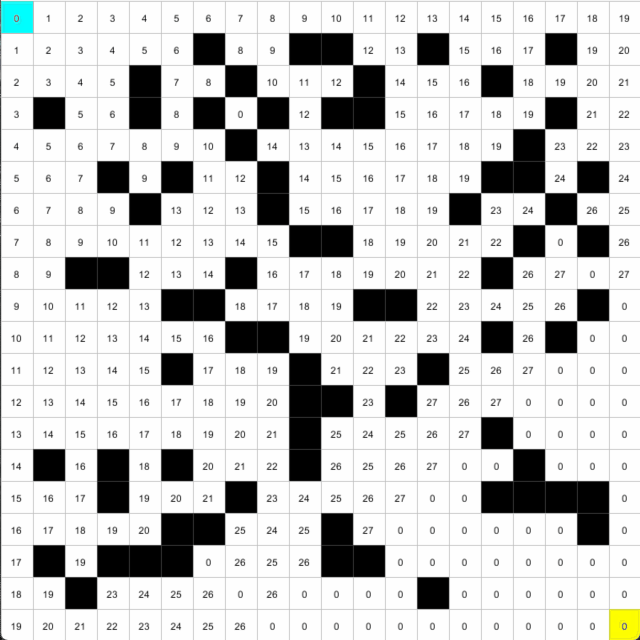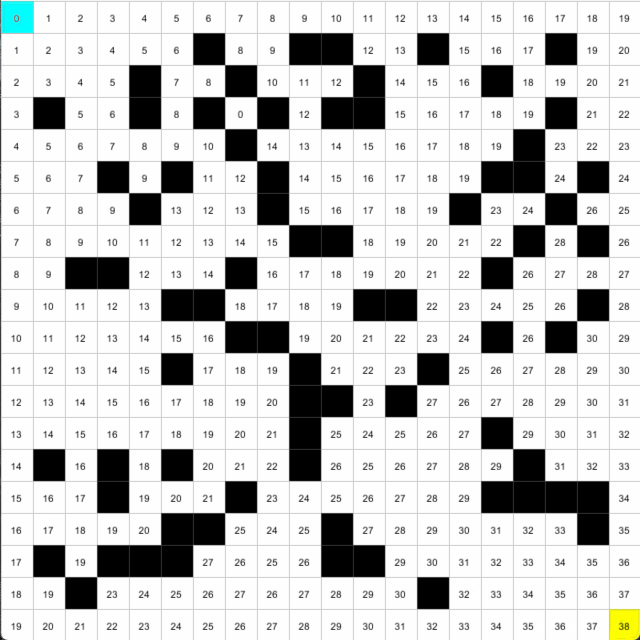
xxxxxxxxxx61cols = rows = 202spots = []3start = end = None4pathIsFound = False5path = []6queue = []這一步我們要先準備前置工作。開3個新的變數,pathIsFound用來紀錄路徑是否已經找到。path=[]用來裝起路徑的spot,queue=[]用來裝起待處理的格。
xxxxxxxxxx71class Spot:2
3 def __init__(self, _i, _j):4 #(same as before)5 self.neighbors = []6 self.visited = False7 self.score = 0在spot class中,加入self.visited = False用來紀錄這格是否已經計算過,self.score = 0用來紀錄這一格的分數。
xxxxxxxxxx101def show(self, _color):2 strokeWeight(0.5)3 stroke(127)4 if self.wall:5 fill(0)6 else:7 fill(_color)8 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)9 fill(0)10 text(self.score, self.x, self.y)在show()中,將分數顯示在畫面上。
xxxxxxxxxx51 def visit(self):2 self.visited = True3 4 def isVisited(self):5 return self.visited最後加入兩個函數,用來設定已訪問過和回傳是否訪問過。
xxxxxxxxxx231def setup():2 global spots, start, end3 #(same as before)4 5 start.visit()6 queue.append(start)7
8def draw():9 global pathIsFound, path, queue10 11 if len(queue) == 0:12 noLoop()13 return14
15 background(51)16
17 current = queue.pop(0)18 19 for neighbor in current.neighbors:20 if not neighbor.isVisited() and not neighbor.wall:21 neighbor.visit()22 neighbor.score = current.score + 123 queue.append(neighbor)在setup()中,先將start設定成已訪問過,並放入queue候選列。
在draw()中,將queue候選列中的第一個用pop釋放出來作為current,之後查找這個current的鄰居,如果沒有到訪過而且也不是牆的話,就將其設定成已訪問,並且為它的分數設成current.score + 1,再將這個鄰居放入queue候選列。
最後,在draw()的最上方,加入如果queue候選列長度為零(即已將所有鄰居都找查完,就設成noLoop()和return。
4. 找出路徑
xxxxxxxxxx1141# A demo about wavefront algorithm2
3cols = rows = 204spots = []5start = end = None6pathIsFound = False7path = []8queue = []9
10def setup():11 global spots, start, end12 size(800, 800)13 textAlign(CENTER, CENTER)14 rectMode(CENTER)15 spots = [[Spot(i, j) for j in range(rows)] for i in range(cols)]16 17 start = spots[0][0]18 end = spots[cols-1][rows-1]19 20 for i in range(cols):21 for j in range(rows):22 if spots[i][j] != start and spots[i][j] != end:23 spots[i][j].addWall()24 spots[i][j].addNeighbors(spots)25
26 start.visit()27 queue.append(start)28
29
30def draw():31 global pathIsFound, path, queue32 33 if len(queue) == 0:34 noLoop()35 return36
37 background(51)38
39 current = queue.pop(0)40 41 for neighbor in current.neighbors:42 if neighbor == end:43 pathIsFound = True44 print('Avrrived at the end!')45 path.append(neighbor)46 path.append(current)47 while current != start:48 for neighbor in current.neighbors:49 if neighbor.score == current.score - 1 and not neighbor.wall:50 path.append(neighbor)51 current = neighbor52 break53 print('Path is found!')54 noLoop()55 else: 56 if not neighbor.isVisited() and not neighbor.wall:57 neighbor.visit()58 neighbor.score = current.score + 159 queue.append(neighbor)60
61 for i in range(cols):62 for j in range(rows):63 spots[i][j].show('#FFFFFF')64 for spot in path:65 spot.show('#FF00FF')66 start.show('#00FFFF')67 end.show('#FFFF00')68
69
70
71class Spot:72
73 def __init__(self, _i, _j):74 self.w = width/cols75 self.h = height/rows76 self.i = _i77 self.j = _j78 self.x = _i * self.w + self.w/279 self.y = _j * self.h + self.h/280 self.wall = False81 self.neighbors = []82 self.visited = False83 self.score = 084
85 def show(self, _color):86 strokeWeight(0.5)87 stroke(127)88 if self.wall:89 fill(0)90 else:91 fill(_color)92 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)93 fill(0)94 text(self.score, self.x, self.y)95
96 def addWall(self):97 self.wall = True if random(1) < 0.25 else False98
99 def addNeighbors(self, _spots):100 if self.wall == False:101 if self.j > 0 and _spots[self.i][self.j-1].wall == False:102 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i][self.j-1])103 if self.i < cols-1 and _spots[self.i+1][self.j].wall == False:104 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i+1][self.j])105 if self.j < rows-1 and _spots[self.i][self.j+1].wall == False:106 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i][self.j+1])107 if self.i > 0 and _spots[self.i-1][self.j].wall == False:108 self.neighbors.append(_spots[self.i-1][self.j])109 110 def visit(self):111 self.visited = True112 113 def isVisited(self):114 return self.visited
xxxxxxxxxx191 for neighbor in current.neighbors:2 if neighbor == end:3 pathIsFound = True4 print('Avrrived at the end!')5 path.append(neighbor)6 path.append(current)7 while current != start:8 for neighbor in current.neighbors:9 if neighbor.score == current.score - 1 and not neighbor.wall:10 path.append(neighbor)11 current = neighbor12 break13 print('Path is found!')14 noLoop()15 else: 16 if not neighbor.isVisited() and not neighbor.wall:17 neighbor.visit()18 neighbor.score = current.score + 119 queue.append(neighbor)在draw()之中,在之前為每個鄰居都打分數的步驟之上,加入: 如果找到鄰居就是終點要怎樣做。
在打分數時,我們由起點開始,洪水式擴散出去,每走一步就將score加一,直到找到終點。要在終點找到路返回起點,我們只需要順著分數,在4個鄰居中選取累減的數字,就一定是返回原點的路線。
所以我們首先將neighbor和current加入path中,之後再找出鄰居的鄰居,如果是累減的分數,就將其加入path,再將這個鄰居變成current。
考考你: 將效果美化一下

試著將程式美化到我這個效果。我是將每個spot的分數score用map,根據位置去變成不同顏色color(map(spots[i][j].score, 0, cols+rows, 0, 255),記得要先在setup()設定成colorMode(HSN, 255)。